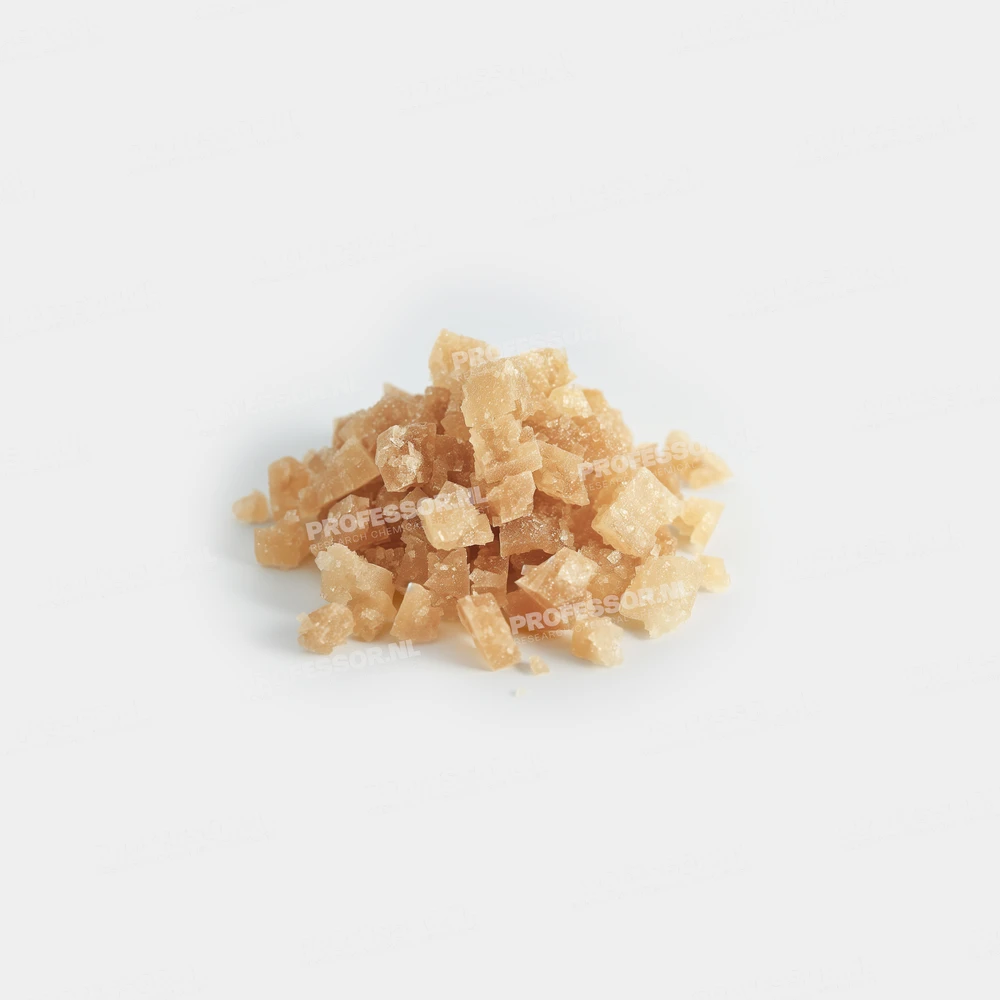
5-MeO-DMT freebase
5-MeO-DMT freebase properties
Synonym: 5-methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine
CAS Number: 1019-45-0
Formula: 3-[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl]-5-methoxyindole
Molar Mass: 218.3 g/mol
Purity: >97%
€25.00 – €700.00Price range: €25.00 through €700.00
* The information on this page is a summary and is not intended to cover all available information about this medication. It does not cover all possible uses, directions, precautions, drug interactions or adverse effects and is not a substitute for the expertise and judgment of your healthcare professional.
5-MeO-DMT Freebase – Scientific Product Documentation
General Description
5-MeO-DMT (5-Methoxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine) freebase is a naturally occurring tryptamine with a potent psychoactive profile, found in various plants and animal secretions. In its freebase form, it offers superior volatility for certain research methods, making it valuable for pharmacological and neuroscience studies.
Technical Specifications
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | C₁₃H₁₈N₂O |
| Molecular Weight | 218.29 g/mol |
| Purity | ≥98% (HPLC-UV analyzed) |
| Form | Crystalline/white powder |
| Solubility | Soluble in organic solvents (ethanol, methanol, DMSO), limited in water |
| Melting point | 60-65°C (freebase) |
| Stability | Light and oxygen sensitive; store under inert gas |
Scientific Applications
1. Neuropharmacological Research
Serotonergic Action: Potent 5-HT₁ₐ/₂ₐ agonist, relevant for studies of consciousness modulation.
EEG/fMRI studies: Research into acute effects on brain wave patterns (e.g. gamma oscillations).
Neuroplasticity: Possible BDNF-enhancing effects (in animal models).
2. Metabolic & Toxicological Studies
MAO-dependent metabolism: Investigation of CYP2D6 and MAO-A degradation pathways.
Dose-dependent toxicity: Determination of safety margins in cell cultures.
3. Comparative Pharmacology
To DMT: Higher potency but shorter duration of action (15-30 min when inhaled).
Regarding psilocybin: Differences in receptor affinity and subjective effects.
Experimental Guidelines
Recommended Concentrations (In Vitro)
| Application | Concentration range | Solvent |
|---|---|---|
| Receptor binding assays | 1 nM – 10 µM | PBS/DMSO (≤0.1%) |
| Cell culture experiments | 0.1 – 100 µM | DMEM/FBS |
| Gas chromatography | 1 mg/ml (in methanol) | Methanol (HPLC grade) |
Safety Protocols
Personal Protection: Lab coat, nitrile gloves, safety glasses, FFP2 mask when handling powder.
Ventilation: Always work under a fume cupboard when heating/evaporating.
Storage: In amber vials, under argon, at -20°C (long term).
Stability & Storage
Shelf life:
Room temperature: <24 hours in solution.
4°C: stable for 3 days (under argon).
-20°C: >6 months (unchanged purity).
Degradation products:
Oxidation to indole derivatives (check by TLC/HPLC).
Analytical Certification
Each batch includes:
HPLC-UV chromatogram (λ=280 nm, C18 column)
GC-MS confirmation (characteristic fragments: m/z 174, 160)
Residual solvent analysis (≤500 ppm)
Water content (Karl Fischer, <1%)
Legal Status (Netherlands)
Opium Act: Not explicitly regulated, but possibly under analogous legislation.
Legislation: License required for scientific institutions (Appendix 2, Opium Act).
Export restrictions: CITES list (due to natural sources such as Incilius alvarius).
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the difference between freebase and fumaric acid salt?
A: Freebase is more volatile (suitable for evaporation experiments), while the fumaric acid salt is more stable for solutions.
Q2: How is 5-MeO-DFT detected in toxicology screens?
A: Recognizable via:
LC-MS/MS (precursor ion m/z 219 → product ion m/z 174)
Immunoassays: Cross-reactivity with some DMT tests (≤30%).
Q3: Are there any known pharmacokinetic interactions?
A: Dangerous combinations:
MAO inhibitors (risk of serotonin syndrome).
SSRIs (reduced efficacy due to competition).
Q4: How to handle waste?
A: Inactivate with:
Dilute hydrochloric acid (0.1M) for neutralization.
Absorption with activated carbon.
Dispose of as hazardous chemical waste (UN number: 3249).
References & Contact
Key publications:
Szára, S. (2007). “DMT and 5-MeO-DMT: Early human studies”.
Uthaug et al. (2021). “Psychopharmacology of 5-MeO-DMT”.
This product is intended for legitimate scientific research only. Not for human or veterinary use. Users should comply with all local regulations.


